Muscle Metabolism
Dublin Core
Title
Subject
Description
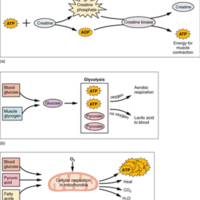
(a) Some ATP is stored in a resting muscle. As contraction starts, it is used up in seconds. More ATP is generated from creatine phosphate for about 15 seconds. (b) Each glucose molecule produces two ATP and two molecules of pyruvic acid, which can be used in aerobic respiration or converted to lactic acid. If oxygen is not available, pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid, which may contribute to muscle fatigue. This occurs during strenuous exercise when high amounts of energy are needed but oxygen cannot be sufficiently delivered to muscle. (c) Aerobic respiration is the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Approximately 95 percent of the ATP required for resting or moderately active muscles is provided by aerobic respiration, which takes place in mitochondria.
Contributor
Cut Rita Zahara
Rights
Creative Commons
Type
Files
Collection
Citation
“Muscle Metabolism ,” Open Educational Resources (OER) , accessed December 19, 2025, https://oer.uinsyahada.ac.id/items/show/1129.