Skeletal Muscle Contraction
Dublin Core
Subject
Description
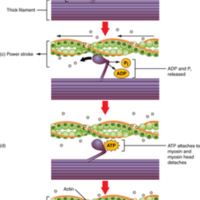
(a) The active site on actin is exposed as calcium binds to troponin. (b) The myosin head is attracted to actin, and myosin binds actin at its actin-binding site, forming the cross-bridge. (c) During the power stroke, the phosphate generated in the previous contraction cycle is released. This results in the myosin head pivoting toward the center of the sarcomere, after which the attached ADP and phosphate group are released. (d) A new molecule of ATP attaches to the myosin head, causing the cross-bridge to detach. (e) The myosin head hydrolyzes ATP to ADP and phosphate, which returns the myosin to the cocked position.
Contributor
Cut Rita Zahara
Rights
Creative Commons
Type
Files
Collection
Citation
“Skeletal Muscle Contraction ,” Open Educational Resources (OER) , accessed January 27, 2026, http://oer.uinsyahada.ac.id/items/show/1128.